Cho hình bình hành ABCD có M là trung điểm của BC, G là trọng tâm tam giác ABC. Chứng minh: \(\overrightarrow{BD}+\overrightarrow{2AM}=\overrightarrow{3GC}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
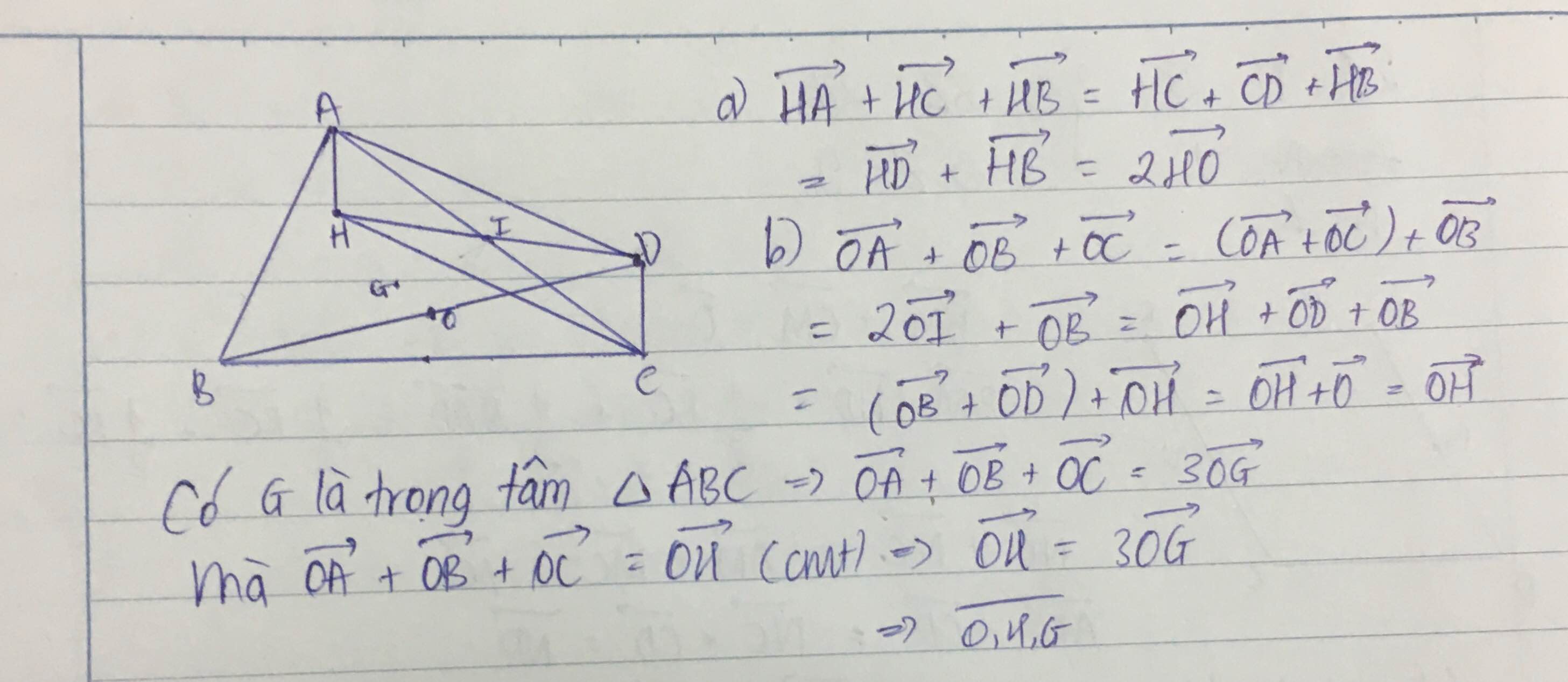
Cho tam giác ABC nội tiếp trong đường tròn tâm O. Gọi G,H lần lượt là trọng tâm, trực tâm của tam giác ABC, D là điểm đối xứng với B qua O. a. Chứng minh AHCD là hình bình hành. Suy ra overrightarrow{HA}+overrightarrow{HB}+overrightarrow{HC}2overrightarrow{HO}. b. Chứng minh: overrightarrow{OA}+overrightarrow{OB}+overrightarrow{OC}overrightarrow{OH}. Suy ra O,G,H thẳng hàng. Giúp mình với ạ
Đọc tiếp
Cho tam giác ABC nội tiếp trong đường tròn tâm O. Gọi G,H lần lượt là trọng tâm, trực tâm của tam giác ABC, D là điểm đối xứng với B qua O. a. Chứng minh AHCD là hình bình hành. Suy ra \(\overrightarrow{HA}+\overrightarrow{HB}+\overrightarrow{HC}=2\overrightarrow{HO}\). b. Chứng minh: \(\overrightarrow{OA}+\overrightarrow{OB}+\overrightarrow{OC}=\overrightarrow{OH}\). Suy ra O,G,H thẳng hàng. Giúp mình với ạ
Cho ABCD là hình bình hành. Đặt \(\overrightarrow {AB} = \overrightarrow a ,\overrightarrow {AD} = \overrightarrow b .\) Gọi G là trọng tâm của tam giác ABC. Biểu thị các vecto \(\overrightarrow {AG} ,\overrightarrow {CG} \) theo hai vecto \(\overrightarrow a ,\overrightarrow b .\)
Cách 1:
Gọi O là giao điểm của AC và BD.

Ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AG} = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {BG} = \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow {BG} ;\\\overrightarrow {CG} = \overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {BG} = \overrightarrow {DA} + \overrightarrow {BG} = - \overrightarrow b + \overrightarrow {BG} ;\end{array}\)(*)
Lại có: \(\overrightarrow {BD} =\overrightarrow {BA} + \overrightarrow {AD} = - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b \).
\(\overrightarrow {BG} ,\overrightarrow {BD} \) cùng phương và \(\left| {\overrightarrow {BG} } \right| = \frac{2}{3}BO = \frac{1}{3}\left| {\overrightarrow {BD} } \right|\)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {BG} = \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {BD} = \frac{1}{3}\left( { - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right)\)
Do đó (*) \( \Leftrightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AG} = \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow {BG} = \overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\left( { - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right) = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\\\overrightarrow {CG} = -\overrightarrow b + \overrightarrow {BG} = -\overrightarrow b + \frac{1}{3}\left( { - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right) = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\;\overrightarrow {CG} = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b .\)
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cách 2:
Gọi AE, CF là các trung tuyến trong tam giác ABC.
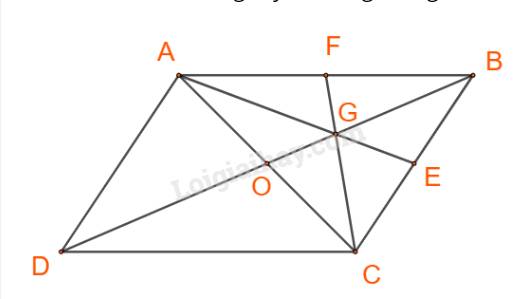
Ta có:
\(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {AE} = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} } \right) = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left[ {\overrightarrow {AB} + \left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} } \right)} \right] \\= \frac{1}{3}\left( {2\overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right) = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b \)
\(\overrightarrow {CG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {CF} = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {CA} + \overrightarrow {CB} } \right) = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left[ {\left( {\overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} } \right) + \overrightarrow {CB} } \right] = \frac{1}{3}\left( {2\overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} } \right) = \frac{1}{3}\left( { - 2\overrightarrow {AD} - \overrightarrow {AB} } \right) = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b \)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\;\overrightarrow {CG} = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b .\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho hình bình hành ABCD. Gọi E là điểm thỏa mãn 4 overrightarrow{DE} overrightarrow{DC} và G là trọng tâm tam giác ABE. Đường thẳng AG cắt BC tại F. Biểu diễn overrightarrow{AG} theo overrightarrow{AB} , overrightarrow{AD} và tính tỉ số dfrac{BF}{BC}
Đọc tiếp
Cho hình bình hành ABCD. Gọi E là điểm thỏa mãn 4 \(\overrightarrow{DE}\) = \(\overrightarrow{DC}\) và G là trọng tâm tam giác ABE. Đường thẳng AG cắt BC tại F. Biểu diễn \(\overrightarrow{AG}\) theo \(\overrightarrow{AB}\) , \(\overrightarrow{AD}\) và tính tỉ số \(\dfrac{BF}{BC}\)
Câu 1: Cho tam giác ABC. Gọi M là trung điểm của BC va G là trọng tâm tâm giác. Kéo dài GM một đoạn MDGMa. Chứng minh : overrightarrow{BD}overrightarrow{GC};overrightarrow{BG}overrightarrow{DC}b. Tìm các vectơ đối của overrightarrow{MD}Câu 2: Gọi AM là trung tuyến của tam giác ABC. Vẽ overrightarrow{BD}overrightarrow{AC}. Chứng minh rằng:a. overrightarrow{AB}overrightarrow{CD};overrightarrow{AM}overrightarrow{MD};overrightarrow{BM}overrightarrow{MC}b. overrightarrow{AM}-overrightarrow{DM};overri...
Đọc tiếp
Câu 1: Cho tam giác ABC. Gọi M là trung điểm của BC va G là trọng tâm tâm giác. Kéo dài GM một đoạn MD=GM
a. Chứng minh : \(\overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{GC};\overrightarrow{BG}=\overrightarrow{DC}\)
b. Tìm các vectơ đối của \(\overrightarrow{MD}\)
Câu 2: Gọi AM là trung tuyến của tam giác ABC. Vẽ \(\overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{AC}\). Chứng minh rằng:
a. \(\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{CD};\overrightarrow{AM}=\overrightarrow{MD};\overrightarrow{BM}=\overrightarrow{MC}\)
b. \(\overrightarrow{AM}=-\overrightarrow{DM};\overrightarrow{MB}=-\overrightarrow{MC}\)
a) Cho tứ giác ABCD không phải là hình bình hành, AC cắt BD tại O có OB OD. Gọi M, N lần lượt là trung điểm của AB và CD, MN cắt AC tại I. Chứng minh rằng overrightarrow{MI}overrightarrow{IN}b) Cho tứ giác ABCD có 2 đường chéo cắt nhau tại I. Biết overrightarrow{IA}+overrightarrow{IB}+overrightarrow{IC}+overrightarrow{ID}overrightarrow{0}. Chứng minh rằng tứ giác ABCD là hình bình hành
Đọc tiếp
a) Cho tứ giác ABCD không phải là hình bình hành, AC cắt BD tại O có OB = OD. Gọi M, N lần lượt là trung điểm của AB và CD, MN cắt AC tại I. Chứng minh rằng \(\overrightarrow{MI}=\overrightarrow{IN}\)
b) Cho tứ giác ABCD có 2 đường chéo cắt nhau tại I. Biết \(\overrightarrow{IA}+\overrightarrow{IB}+\overrightarrow{IC}+\overrightarrow{ID}=\overrightarrow{0}\). Chứng minh rằng tứ giác ABCD là hình bình hành
Cho hình bình hành ABCD tâm O. Xác định vị trí điểm M thỏa mãn \(\overrightarrow{OB}+\overrightarrow{OC}=\overrightarrow{AM}\). Cho tam giác ABC. Gọi M, N, P lần lượt là trung điểm các cạnh AB, BC, CA và dựng điểm K sao cho \(\overrightarrow{MK}+\overrightarrow{CN}=\overrightarrow{0}\). Khi đó, điểm K trùng với
Bài 1:
Gọi K là trung điểm của BC
ABCD là hình bình hành
=>AC cắt BD tại trung điểm của mỗi đường
=>O là trung điểm chung của AC và BD
Xét ΔCAB có
O,K lần lượt là trung điểm của CA,CB
=>OK là đường trung bình
=>OK//AB và \(OK=\dfrac{AB}{2}\)
=>\(\overrightarrow{OK}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{AB}}{2}\)
=>\(\overrightarrow{AB}=2\cdot\overrightarrow{OK}\)
Xét ΔOBC có OK là đường trung tuyến
nên \(\overrightarrow{OB}+\overrightarrow{OC}=2\cdot\overrightarrow{OK}\)
=>\(\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{OB}+\overrightarrow{OC}\)
=>M trùng với B
Bài 2:
Xét ΔABC có
M,P lần lượt là trung điểm của AB,AC
=>MP là đường trung bình của ΔABC
=>MP//BC và MP=BC/2
=>MP=CN
mà MP//NC
nên MPCN là hình bình hành
=>\(\overrightarrow{MP}=\overrightarrow{NC}\)
=>\(\overrightarrow{MP}=-\overrightarrow{CN}\)
=>\(\overrightarrow{MP}+\overrightarrow{CN}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
mà \(\overrightarrow{MK}+\overrightarrow{CN}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
nên K trùng với P
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho tứ giác ABCD có M, N lần lượt là trung điểm của hai cạnh AB và CD. Gọi G là trung điểm của đoạn thẳng MN, E là trọng tâm tam giác BCD. Chứng minh:a) overrightarrow {EA} + overrightarrow {EB} + overrightarrow {EC} + overrightarrow {ED} 4overrightarrow {EG} b) overrightarrow {EA} 4overrightarrow {EG} c) Điểm G thuộc đoạn thẳng AE và overrightarrow {AG} frac{3}{4}overrightarrow {AE}
Đọc tiếp
Cho tứ giác ABCD có M, N lần lượt là trung điểm của hai cạnh AB và CD. Gọi G là trung điểm của đoạn thẳng MN, E là trọng tâm tam giác BCD. Chứng minh:
a) \(\overrightarrow {EA} + \overrightarrow {EB} + \overrightarrow {EC} + \overrightarrow {ED} = 4\overrightarrow {EG} \)
b) \(\overrightarrow {EA} = 4\overrightarrow {EG} \)
c) Điểm G thuộc đoạn thẳng AE và \(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{3}{4}\overrightarrow {AE} \)
a) Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {EA} + \overrightarrow {EB} + \overrightarrow {EC} + \overrightarrow {ED} \)\( = 4\overrightarrow {EG} + \overrightarrow {GA} + \overrightarrow {GB} + \overrightarrow {GC} + \overrightarrow {GD} \)
Mà: \(\overrightarrow {GA} + \overrightarrow {GB} = 2\overrightarrow {GM} ;\) (do M là trung điểm của AB)
\(\overrightarrow {GC} + \overrightarrow {GD} = 2\overrightarrow {GN} \) (do N là trung điểm của CD)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {EA} + \overrightarrow {EB} + \overrightarrow {EC} + \overrightarrow {ED} = 4\overrightarrow {EG} + 2(\overrightarrow {GM} + \overrightarrow {GN} ) = 4\overrightarrow {EG} \) (do G là trung điểm của MN)
b) Vì E là trọng tâm tam giác BCD nên \(\overrightarrow {EB} + \overrightarrow {EC} + \overrightarrow {ED} = \overrightarrow 0 \)
Từ ý a ta suy ra \(\overrightarrow {EA} = 4\overrightarrow {EG} \)
c) Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {EA} = 4\overrightarrow {EG} \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow {EA} = 4.(\overrightarrow {EA} + \overrightarrow {AG} ) \Leftrightarrow - 3\overrightarrow {EA} = 4\overrightarrow {AG} \)
\( \Leftrightarrow 3\overrightarrow {AE} = 4\overrightarrow {AG} \) hay \(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{3}{4}\overrightarrow {AE} \)
Suy ra A, G, E thẳng hàng và \(AG = \frac{3}{4}AE \) nên G thuộc đoạn AE.
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho hình hộp ABCD.A'B'C'D' có P và R lần lượt là trung điểm các cạnh AB và A'D'. Gọi P', Q,Q',R' lần lượt là tâm đối xứng của các hình bình hành ABCD, CDD'C', A'B'C'D', ADD'A'
a) Chứng minh rằng \(\overrightarrow{PP'}+\overrightarrow{QQ'}+\overrightarrow{RR'}=\overrightarrow{O}\)
b) Chứng minh hai tam giác PQR và P'Q'R' có trọng tâm trùng nhau
Cho A(1;3); B(2;-4); C(-3;5); D(-4;-5)
a) Tìm M sao cho \(2\overrightarrow{AM}+3\overrightarrow{AB}-4\overrightarrow{AC}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
b) Tìm D sao cho tứ giác ADIG là hình bình hành với G trọng tâm tam giác ABC, I trung điểm AC.
c) Tìm giao điểm của hai đoạn thẳng AB và CD